image from : linkedin.com
Introduction
Energy efficiency is no longer just a buzzword—it is a necessity in today’s rapidly changing world. Rising energy costs, growing environmental concerns, and the demand for sustainable development are pushing homeowners, industries, and building managers to adopt innovative solutions that save energy and reduce emissions.
In fact, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), energy efficiency improvements could account for more than 40% of the emissions reductions needed to meet global climate goals. The good news is that technology and smart strategies are making efficiency easier, more affordable, and more impactful than ever before.
This article explores cutting-edge technologies and practical strategies for energy efficiency across three main sectors: homes, industries, and commercial buildings.
Why Energy Efficiency Matters
Before diving into the specific technologies, it’s important to understand why efficiency should be a top priority.
-
Cost Savings – Lower electricity bills and reduced maintenance costs.
-
Environmental Benefits – Less greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
-
Energy Security – Reduced dependence on fossil fuels and improved resilience against energy crises.
-
Increased Property Value – Energy-efficient homes and buildings are often more attractive to buyers and tenants.
-
Regulatory Compliance – Many countries are tightening energy regulations, making efficiency not only desirable but mandatory.
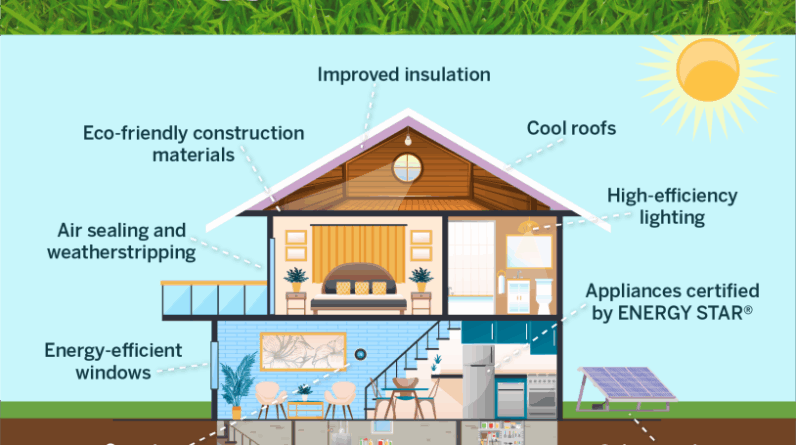
Energy Efficiency in Homes
1. Smart Home Technologies
Modern smart homes are designed to reduce energy waste automatically. Some of the most effective solutions include:
-
Smart Thermostats: Devices like Nest or Ecobee learn household habits and adjust heating/cooling accordingly, cutting energy use by up to 15%.
-
Smart Lighting Systems: LED bulbs combined with motion sensors and timers can significantly reduce wasted electricity.
-
Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS): Platforms that monitor and optimize electricity consumption in real time.
2. Energy-Efficient Appliances
Switching to appliances with an Energy Star rating or equivalent certifications ensures lower energy consumption. Efficient refrigerators, washing machines, and dishwashers can reduce household energy bills by 20–30%.
3. Insulation and Building Materials
-
Double- or Triple-Glazed Windows reduce heat loss.
-
Insulated Walls and Roofs maintain stable indoor temperatures.
-
Cool Roof Technology reflects more sunlight and absorbs less heat, cutting cooling costs.
4. Renewable Energy Integration
Homeowners are increasingly adopting solar panels, solar water heaters, and even small-scale wind turbines to reduce dependence on grid electricity. Coupled with battery storage systems, these solutions enhance both efficiency and resilience.
Energy Efficiency in Industries
1. Industrial Automation and IoT
Factories are adopting Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies to track, analyze, and optimize energy consumption. Sensors and AI-driven analytics detect inefficiencies and suggest corrective actions in real time.
For example, smart motors and variable frequency drives (VFDs) adjust motor speed to demand, avoiding unnecessary energy use.
2. Waste Heat Recovery Systems
Many industries release massive amounts of heat as a byproduct. Technologies like heat exchangers, cogeneration (CHP), and organic Rankine cycles capture this heat and repurpose it for other processes, improving overall efficiency.
3. Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
-
Lean Manufacturing eliminates unnecessary steps that consume energy.
-
Green Supply Chains ensure efficiency from raw materials to final products.
-
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing) reduces waste compared to traditional methods.
4. Renewable Energy in Industry
Large industrial players are investing in onsite solar, wind, or biomass energy systems. For example, Tesla’s Gigafactories rely heavily on renewable energy to meet massive power demands while reducing operational costs.
5. Energy Management Standards
Standards like ISO 50001 provide a structured framework for organizations to manage energy performance. Companies that adopt these standards often see efficiency improvements of 10–20% within the first few years.
Energy Efficiency in Commercial and Public Buildings
1. Smart Building Management Systems (BMS)
Modern buildings are increasingly “intelligent.” A Building Management System (BMS) integrates lighting, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), security, and energy monitoring into a single automated platform.
2. Energy-Efficient HVAC Systems
-
Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems adjust airflow based on occupancy.
-
Geothermal Heating and Cooling taps into stable underground temperatures for efficiency.
-
Chilled Beams use water to cool spaces more efficiently than traditional air systems.
3. Lighting Innovations
-
Daylight Harvesting Systems adjust artificial lighting based on available natural sunlight.
-
LED Retrofits can cut lighting costs by 60–80%.
4. Green Building Certifications
-
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM certifications encourage energy-efficient design.
-
Certified buildings not only save energy but also attract environmentally conscious tenants and investors.
5. Occupant Engagement
Even the most advanced technology won’t deliver results if building occupants don’t cooperate. Programs that educate and incentivize energy-saving behaviors—like turning off unused equipment—are essential.
Cutting-Edge Energy Technologies to Watch
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Energy Management – AI predicts energy demand, optimizes loads, and prevents waste.
-
Blockchain for Energy Trading – Decentralized systems allow homeowners and businesses to sell excess renewable power securely.
-
Advanced Energy Storage – Lithium-ion and solid-state batteries enable better integration of renewables.
-
Microgrids – Localized power systems enhance resilience and reduce transmission losses.
-
Green Hydrogen – A promising energy carrier for industries and transportation.
Practical Strategies for Every Sector
Regardless of whether it’s a home, factory, or office tower, some strategies work universally:
-
Conduct Regular Energy Audits – Identify inefficiencies and set measurable targets.
-
Switch to Renewable Energy Sources – Even partial integration reduces costs and emissions.
-
Invest in Staff or Occupant Training – Human behavior can make or break efficiency efforts.
-
Adopt Automation & Smart Systems – Real-time monitoring and control minimize waste.
-
Set Long-Term Sustainability Goals – Efficiency is not a one-time effort but an ongoing journey.
Future Outlook
The future of energy efficiency lies in the convergence of digital technology, renewable energy, and smart infrastructure. By 2030, global investments in efficiency are expected to exceed trillions of dollars, creating not only greener environments but also new economic opportunities.
Governments worldwide are offering incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks to push adoption. As technology advances and costs drop, energy efficiency will no longer be optional—it will be standard.
Conclusion
Energy efficiency is one of the most powerful tools we have to fight climate change, cut costs, and secure a sustainable future. Whether at home, in industries, or in large buildings, the combination of innovative technologies and smart strategies can deliver massive benefits.
By investing in energy-efficient solutions today, we can create a more sustainable, cost-effective, and resilient tomorrow.